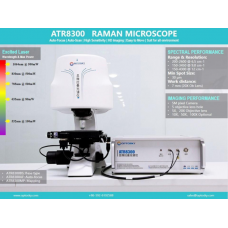
The ATR8800UV Confocal Raman Microscope is a cutting-edge scientific-grade instrument that integrates four lasers and combines the advantages of a microscope with a Raman spectrometer. It includes UV wavelengths of 266nm and 325nm, offering significant advantages for the analysis of fluorescence-resistant materials and samples with complex structures. This advanced Raman microscope provides high-resolution analysis for a wide range of materials, including graphene, nanomaterials, thin films, semiconductors, and biological tissues.
The ATR8800UV can visually and accurately locate the Raman detection platform, enabling precise detection of Raman signals from various surface states. The system displays the microzoning shape of the detected positions on the computer, enhancing the efficiency of Raman micro-area detection.
This UV Raman Imaging Microscope features fully auto-focus and auto-scanning for continuous scanning, significantly improving the ease of use and reliability of Raman imaging. Whether performing uniform scans or detailed identification, the ATR8800UV ensures highly reliable scanning and imaging of Raman data without delay. The system is equipped with Raman spectrometers of different focal lengths, meeting the demands of high-resolution Raman imaging.
Equipped with Raman-specific objective lenses, the ATR8800UV achieves diffraction-limited laser spots, ensuring accurate focusing and improved Raman spectral quality. The camera system captures focus information precisely and intuitively, with 5-million-pixel cameras that visualize Raman data in real-time. Unlike ordinary systems, the ATR8800UV eliminates slight focal misalignments, enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio and providing superior Raman spectral stability.
In addition, the ATR8800UV resolves the issue of imaging path delays, separating camera imaging from Raman signal collection to maximize signal strength. With high-performance Raman detection, the ATR8800UV sets the standard in UV Raman microscopy, offering exceptional sensitivity, reliability, and industry-leading performance for Raman research and material characterization.
Applications of 266nm and 325nm Raman Spectroscopy
Fluorescence-Resistant Materials: The use of 266nm and 325nm wavelengths is particularly advantageous for samples that are prone to fluorescence interference under conventional visible light Raman excitation. UV wavelengths can reduce the background fluorescence, providing clearer spectra and better resolution in materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, and semiconductors.
Graphene and Nanomaterials: At 266nm, Raman spectroscopy is effective in distinguishing between different graphene layers and characterizing other nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes, where the excitation energy is higher, and the enhanced Raman signal from defects or disorder (e.g., D-band) can be observed with greater precision.
Semiconductors and Thin Films: UV Raman spectroscopy (particularly at 266nm) allows deeper penetration into thin films and semiconductor materials, aiding in the study of strain, defects, and interfaces. For example, silicon, gallium nitride (GaN), and III-V semiconductors benefit from enhanced Raman signals at shorter wavelengths, which improves defect detection and characterization.
Biological Tissues and Cells: The ATR8800UV is particularly valuable in biological studies where UV Raman provides high sensitivity with minimal interference from intrinsic fluorescence. This allows for precise mapping of tissue structures, biomolecules like proteins, and even the study of cellular dynamics in live tissue without invasive labeling.
Polymer and Coatings: UV Raman spectroscopy at both 266nm and 325nm is highly effective in characterizing polymeric materials and coatings, where lower excitation wavelengths enhance the spectral response from polymers and provide better resolution of chemical bonds and structures. It is widely used in material science for quality control and failure analysis of coatings, adhesives, and films.
High-Resolution Surface and Interface Studies: The ability of UV Raman to interact with surface states makes it ideal for examining surfaces and interfaces of materials. This is crucial for the development of microelectronics, solar cells, and high-performance coatings, where accurate layer analysis at the nanometer scale is required.
Fluorescence-Resistant Materials: The use of 266nm and 325nm wavelengths is particularly advantageous for samples that are prone to fluorescence interference under conventional visible light Raman excitation. UV wavelengths can reduce the background fluorescence, providing clearer spectra and better resolution in materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, and semiconductors.
Graphene and Nanomaterials: At 266nm, Raman spectroscopy is effective in distinguishing between different graphene layers and characterizing other nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes, where the excitation energy is higher, and the enhanced Raman signal from defects or disorder (e.g., D-band) can be observed with greater precision.
Semiconductors and Thin Films: UV Raman spectroscopy (particularly at 266nm) allows deeper penetration into thin films and semiconductor materials, aiding in the study of strain, defects, and interfaces. For example, silicon, gallium nitride (GaN), and III-V semiconductors benefit from enhanced Raman signals at shorter wavelengths, which improves defect detection and characterization.
Biological Tissues and Cells: The ATR8800UV is particularly valuable in biological studies where UV Raman provides high sensitivity with minimal interference from intrinsic fluorescence. This allows for precise mapping of tissue structures, biomolecules like proteins, and even the study of cellular dynamics in live tissue without invasive labeling.
Polymer and Coatings: UV Raman spectroscopy at both 266nm and 325nm is highly effective in characterizing polymeric materials and coatings, where lower excitation wavelengths enhance the spectral response from polymers and provide better resolution of chemical bonds and structures. It is widely used in material science for quality control and failure analysis of coatings, adhesives, and films.
High-Resolution Surface and Interface Studies: The ability of UV Raman to interact with surface states makes it ideal for examining surfaces and interfaces of materials. This is crucial for the development of microelectronics, solar cells, and high-performance coatings, where accurate layer analysis at the nanometer scale is required.
With high-performance Raman detection, the ATR8800UV offers an unparalleled combination of sensitivity, resolution, and reliability, making it the ideal choice for advanced research in material science, nanotechnology, and biology.
| Confocal Raman Microscope | |
| Excitation Wavelength | 266,325,532,638,785, 1064nm Optional |
| Focal Length | 350mm、510mm、760mm Optional |
| Spot Diameter | >1μm |
| Communication Mode | USB2.0 |
| Optical Path | C-T optical path |
| Objective Lens | High UV transmittance objective lens,Standard configuration:4X、 10X、20X; Optional configuration:50X、 100X |
| Focus Method | Conjugate Focus |
| Laser Stability | σ/μ <±0.2% |
| Laser Power | 266nm:50mW 325nm: 30mW 532nm: 100mW 633nm:80mW 638nm: 80mW 785nm:350mW 1064nm:500mW |
| Voltage | 100~240V |
| Peak Power | 100W |
| Dimensions | ATR8800UV-FL210 : 823(L) × 500(W) × 643(H) ATR8800UV-FL350 : 905(L) × 500(W) × 643(H) ATR8800UV-FL510:1009(L)×500(W)×643(H) ATR8800UV-FL760: 1320(L)×500(W)×643(H) |

-600x600.jpg)
-74x74.jpg)